Telecommunications companies are monitoring lasers with infrared cameras to minimise signal loss. Cinogy Technologies in Ruderstadt, Germany has developed laser beam profilers based on short-wave infrared cameras for measuring signal loss from telecom fibre optics.
The profilers are used to monitor parameters such as power, beam position and size, along with laser beam profile.
With a fibre diameter of approximately 6µm, directing a laser beam so that the coupling efficiency - the relationship between the original beam and coupled performance - is optimal, can be a challenge. Live measurements of the beam parameters enable telecom providers to calibrate the beam, optimising performance.
Cinogy’s laser beam profilers for the near infrared range – where telecommunication wavelengths fall – are based upon modern indium-gallium-arsenide (InGaAs) sensors and are equipped with infrared cameras from Allied Vision.
‘With InGaAs-sensor-based laser beam characterisation systems, it is possible for users in the field of telecommunications to carry out laser beam analysis and optimisation in the infrared range, which is not possible with systems based on CCD or CMOS sensors,’ said Andy Kaemling, managing director of Cinogy Technologies.
Cinogy’s systems use Allied Vision Goldeye G-008 SWIR (320 x 256 pixels) or Goldeye G-033 SWIR (640 x 512 pixels) cameras in the laser beam profiler. Both models use a SWIR InGaAs FPA sensor covering the spectral range from 900nm to 1,700nm. The sensors are cooled, which increases their sensitivity while maintaining low background noise, even with long exposure times.
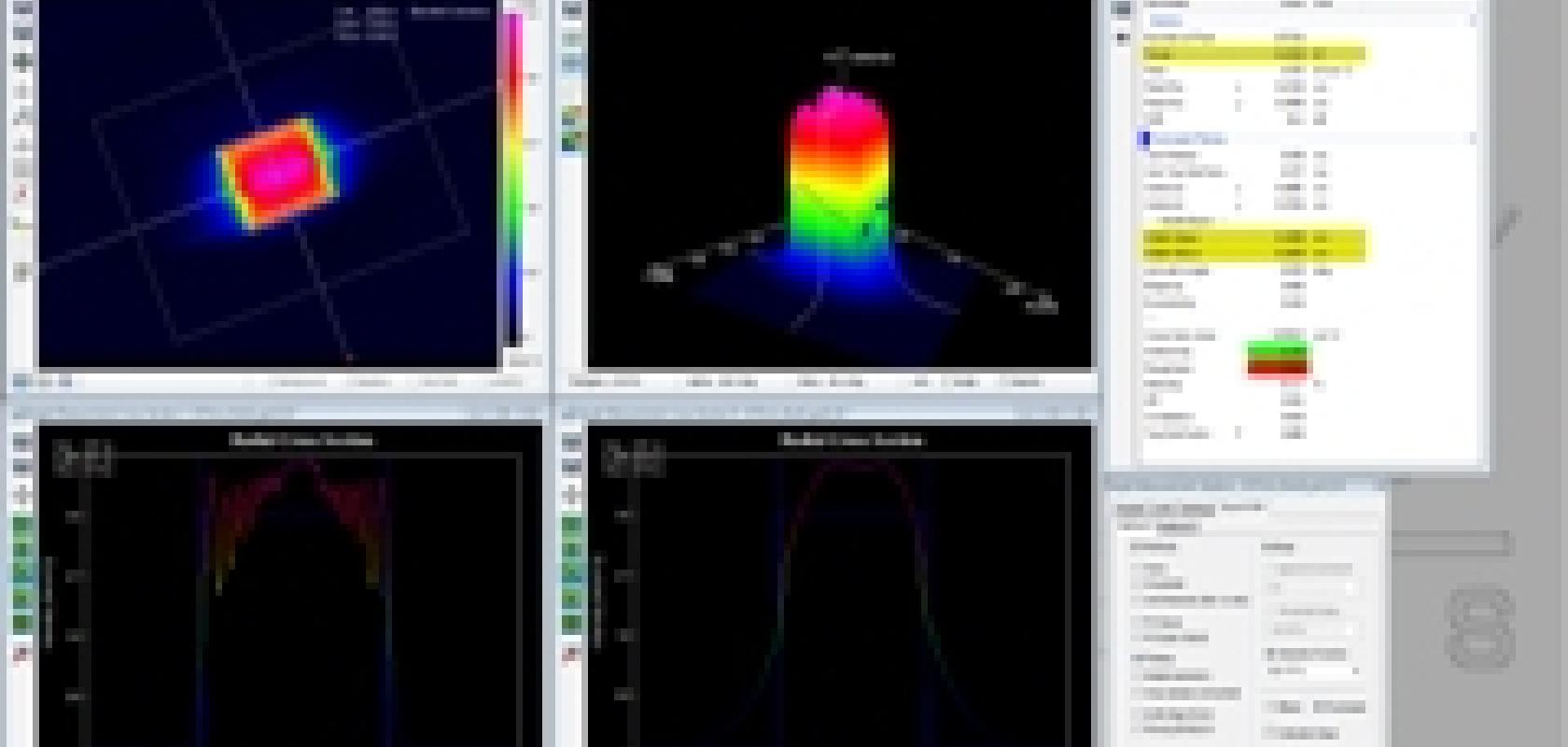
The laser beam is pointed directly onto the InGaAs sensor and analysed using Cinogy’s RayCi analysis software. The program enables continual monitoring of beam parameters, such as coupling efficiency, in real-time. If there are undesired structures in the beam, the laser profile displays signal loss live in the system.
The beam parameters are visualised in two-dimensional profiles that reproduce the form and profile of the beam. Colour-graded scales highlight the different characteristics. The software also offers an XML-RPC interface for remote software control. This enables efficient and simple integration of beam analysis into external applications. Easy implementation into different system platforms via XML commands sets this interface apart.
Laser beam characterisation systems based on InGaAs sensors are already in use worldwide. Cinogy Technologies is currently developing a new measurement system conceived primarily for the infrared range; infrared cameras from Allied Vision will be an integral component.
Further information: